Sweet Potato
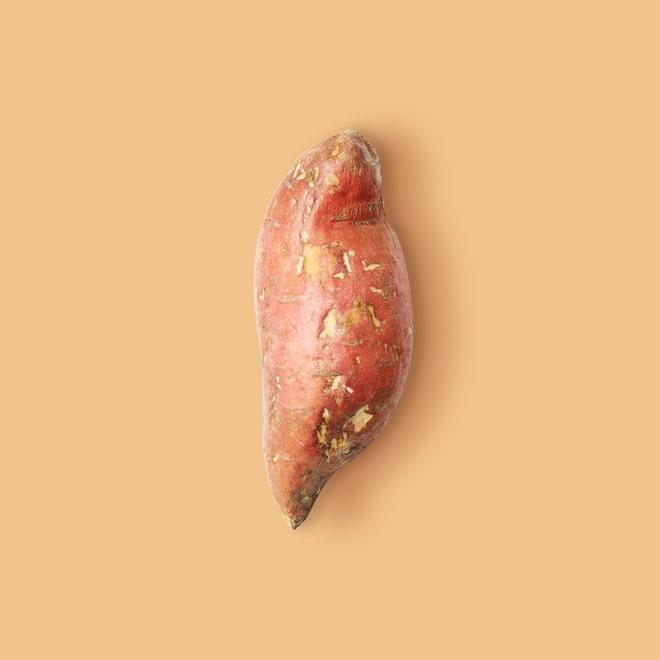



Sweet potatoes are often mistaken as yams, but they are totally different vegetables. They are large, starchy, sweet-tasting root vegetables that can be orange, purple, or white, while yams are larger, yellow-fleshed vegetables with more bark-like skin. To make matters even more complicated, sweet potatoes are roots that are actually related to the morning glory family, not the potato, which are tubers.
Select firm potatoes that are with smooth, unblemished skin.
The ideal location to store sweet potatoes is a cool and dark cabinet or pantry. When stored under these circumstances sweet potatoes can last several months or more.
Due to an enzyme reaction, sweet potatoes dry out and toughen when stored in the refrigerator.
Sweet potato becomes sweet due to the action of an enzyme that breaks down starch. The enzyme then starts to make maltose, which gives the sweet taste to the potato.
George Washington Carver developed over 100 products using sweet potatoes like glue for postage stamps and starch for cotton fabrics.
Sweet potatoes can be used interchangeably with regular potatoes in most recipes.
Sweet potatoes take well to many cooking methods, including baking, frying, roasting, and boiling.
They can even be eaten raw: try grating sweet potato for a nice touch to slaws or salads.
Sweet potatoes make a really creamy and delicious smoothie when combined with frozen banana, dates, cinnamon, vanilla, and milk or water.
Sweet potatoes are a good source of vitamins A, C, E and Beta Carotene
Maximize their nutrition by leaving the skin on when cooking them.
Sweet potatoes have comparatively less calories, fat and sodium than white potatoes, though they do contain more sugar.
Corrections or improvements? Email us at
content@sidechef.com